|
More Muscle Injury Facts:
One common cause of muscle aches and pain is fibromyalgia, a condition that includes tenderness in your muscles and surrounding soft tissue, sleep difficulties, fatigue, and headaches
Muscle pain may also be caused by certain drugs, including ACE inhibitors and statins. ACE inhibitors are widely used for lowering blood pressure and statins for lowering cholesterol
Incomplete healing and re-injury can lead to a build up of scar tissue in the muscle causing further injury.
Home Conservative Guidelines: - Rest
- Use cold reduce pain, swelling.
- Use TShellz Wrap® treatments to increase blood flow in the treatment area.
- Once swelling is reduced and healing has begun, start stretching the injured joint after warming up with a TShellz Wrap®. (stretching=good, straining=bad)
Typical characteristics of a muscle injury are bruising, weakness, muscle tightness and the inability to stretch the area
| Supraspinatus Tendinitis
Supraspinatus Tendinitis is also referred to as Rotator Cuff Tendonitis, Swimmer's Shoulder, Pitcher's Shoulder or Tennis Shoulder.
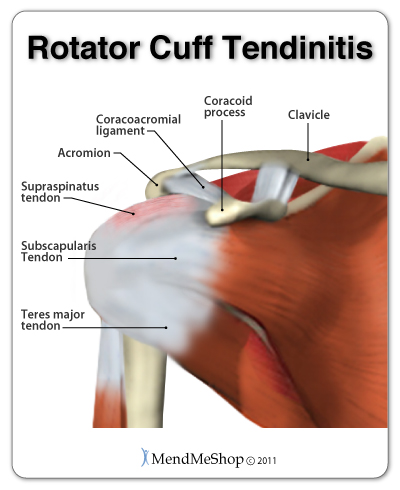
Tendons are bands of connective tissue that join your muscles to your bones. This connection allows you to move your body when you contract your muscles. The rotator cuff (also called the rotor cuff) is made up of 4 tendons located at the outside edge of your shoulder that form a "cuff" around the glenohumeral joint. These tendons, along with other soft tissue in the joint cavity, work together to attach the humerus (upper arm bone) to the scapula. When the shoulder muscles contract, these tendons; the supraspinatus, the infraspinatus, the teres minor and the subscapularis, allow your shoulder to complete its complex set of movements and move your arm.
Tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis) is inflammation in a tendon. When you are diagnosed with rotator cuff tendonitis, it means that one or more of the four tendons in the rotator cuff has become inflamed. The inflammation of tendonitis is usually a result of tiny tears or repetitive irritation of the tendon.
There are 2 types of rotator cuff tendonitis; acute and chronic:
- Acute tendonitis refers to inflammation that comes on suddenly, usually from a shoulder injury, such as a fall causing dislocation (typically a person may even develop Frozen Shoulder), overloading it during exercise, or lifting something too heavy overhead.
- Chronic tendonitis develops over-time and generally results from long term repetitive use of one or some of the rotator cuff tendons. Common activities that cause chronic tendinitis in the rotor cuff are activities like weight lifting, painting, and repetitive throwing in sports. With both types of tendinitis, the condition can be very painful. Likely you have periods where it flares up, and periods when it feels somewhat better after it has been rested or the repetitive motion that irritates it has been stopped.
Although tendinitis can occur in any of the rotator cuff tendons, the supraspinatus tendon is the tendon most at risk of injury. Due to its location at the top of the shoulder - between the joint cavity and the rigid bony arch of the shoulder blade (acromion) - the tendon is at risk from irritation, wear and tear, and/or the nerve becoming trapped in the soft tissues of the shoulder (impingement). The attachment of the muscles and tendons to the acromion provides the leverage that helps to lift the weight of the arm away from the body (abduct). As most of use use our arm for many daily activities, it is a fairly common injury; if this tendon injury is ignored, it will likely worsen and can lead to chronic (long term) tendinitis.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
The symptoms of chronic rotator cuff tendinitis usually begin with mild pain in the shoulder that gradually becomes worse. Acute symptoms will come on more suddenly. If you have rotator cuff tendinitis, some possible symptoms may be:
- Pain in the top and front of your shoulder that becomes worse with overhead activity. Initially, the pain is felt during activities only but eventually you will feel it even while you rest your shoulder.
- Limited range of motion in your shoulder's glenohumeral joint.
- Tenderness and a burning sensation in your shoulder.
- The feeling that the small muscles in the shoulder do not make small adjustments smoothly, or pain that results from these small motions.
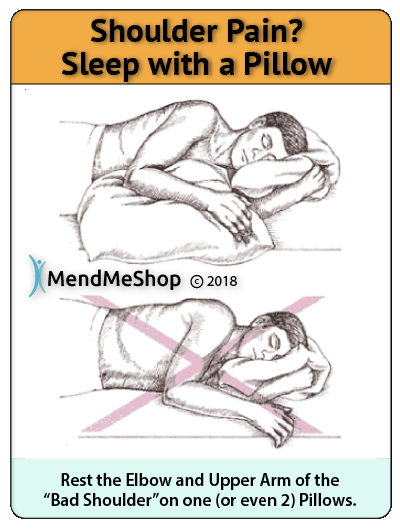
- Difficulty sleeping at night due to pain, especially when lying on the affected shoulder.
- Difficulty with simple movements such as brushing hair, putting on your shirt or jacket, reaching the arm above shoulder height.
- A feeling of weakness in the shoulder, especially with pushing and overhead movements.
If you've suffered a traumatic sudden injury to your shoulder, you may have heard a sudden popping sound or felt a tearing sensation in your shoulder. Swelling around your shoulder will happen within a few hours after the injury or in the following days. If the injury is severe enough, you may also have some bruising on your shoulder. Immediate, intense, pain will follow - especially when you try to raise, lower, or rotate your arm.
If your rotator cuff tear is big enough you might feel weakness (instability) in your shoulder. Over time this weakness will turn into a limited range of motion and inability to raise, lower, or rotate your arm - resulting in pain. At this point your rotator cuff injury would also be interfering with your sleep, causing pain and night and forcing you to wake up several times to adjust your sleeping position.
Degenerative rotator cuff tears are subtle with pain that increases over time. You may also notice swelling after exercise or daily activities. If you do have pain, you may experience something called 'trigger point pain' in your shoulder and possibly feel weakness / instability. Trigger point pain is pain that comes from a specific spot in your rotator cuff muscle that has become a hypersensitive area. These trigger points, or hypersensitive areas of pain, are known to be a source of on-going pain and lack of blood flow within the tissue. Pain may increase with certain activities, like raising your arm to reach for something off of a high shelf, brushing your hair or teeth, getting dressed, or reaching behind your back.
Causes of Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
- A hooked acromion at birth increases your risk of rotator cuff tendinitis and bursitis as they can become impinged in the subacromial space.
- Slouching forward can narrow the space your tendons have to move in the shoulder creating excess pressure on them. This can irritate the tendons and/or interrupt the blood supply resulting in breakdown of the tissue.
- Repetitive overhead motion such as serving a tennis ball, pitching a ball, hammering, or painting above the head.
- Lifting heavy objects or free weights above shoulder height.
- Aging; as we get older, our tendons become more brittle and therefore more prone to injury.
- A weak rotator cuff can cause misalignment, putting unequal stress on the tendons.
- Shoulder injuries or having associated conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disease.
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis Treatments - What You Can Do!
If you have a rotator cuff tendinitis, rest is highly recommended. Avoid activities that cause pain or may have caused the inflammation and begin cold compression treatments as soon as possible.
Your doctor will assess your particular case and determine a course of action. In most cases, a conservative treatment protocol will be enough to heal the injury, though in cases such as significant tearing or a fully ruptured quad, you will most probably require surgery. It is generally understood by doctors and surgeons, that surgery will introduce more scar tissue into the any already damaged tissue. This added scar tissue will be problematic, requiring more physical therapy and conservative treatment options post-surgery. If not dealt with properly, your muscle injury could end up in worse condition than before the surgery! This is why surgery is only performed as a last resort.
To view more information about conservative treatments for quadriceps tendinitis, please go to our rotator cuff tendinitis page on aidyourtendon.com.
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort in your knee area until your pain and inflammation settle.
The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results! We recommend that you consult your doctor and/or physiotherapist before using any of our outstanding products, to make sure they're right for you and your condition.
Learn More About Muscle Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about Post-Surgery Recovery I want to learn more about muscle injury home treatment using the TShellz Wrap® I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Muscle Strains/Spasms? Do I Need Muscle Surgery?
FREE SHIPPING ON ALL PRODUCTS CURRENTLY ENABLED
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. Always consult your doctor and/or Physical Therapist before using any of our outstanding products, to make sure they are right for you and your condition. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results!
Product specialists are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday. If any question or concern arises, call us or simply send us an email at any time (we check our emails constantly all throughout the day and night.. even on holidays!). We will respond as soon as possible. North America Toll Free 1-866-237-9608
Outside North America +1-705-532-1671
|
Muscle Injury Facts:
There are approximately 639 muscles in the human body
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than one muscle
Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia, the soft tissues that connect muscles, bones, and organs
Oral medications can mask the pain but do not aid in the healing of a muscle injury. Anti-inflammatories and pain killers can cause muscle related injuries to worsen
Muscle pain also can be a sign of conditions affecting your whole body, like some infections and disorders that affect connective tissues throughout the body
Most common cause of muscle aches & pains: - Injury or trauma including sprains and strains
- Overuse: using a muscle too much, too soon, too often
- Tension or stress

          |